HOME UNIT 1 UNIT 2 UNIT 3 UNIT 4 UNIT 5
The CoAP
protocol is a web transfer protocol which is used in constrained nodes or
networks such as WSN, IoT, M2M etc. Hence the name Constrained Application
Protocol. The protocol is targeted for Internet of Things (IoT) devices having
less memory and less power specifications.
As it is
designed for web applications it is also known as "The Web of Things
Protocol". It can be used to transport data from few bytes to 1000s of
bytes over web applications. It exists between UDP layer and Application layer.
Following
are the features of CoAP Protocol:
• It is very efficient RESTful protocol.
• Easy to proxy to/from HTTP.
• It is open IETF standard
• It is Embedded web transfer protocol (coap://)
• It uses asynchronous transaction model.
• UDP is binding with reliability and multicast support.
• GET, POST, PUT and DELETE methods are used.
• URI is supported.
• It uses small and simple 4 byte header.
• Supports binding to UDP, SMS and TCP.
• DTLS based PSK, RPK and certificate security is used.
• uses subset of MIME types and HTTP response codes.
• Uses built in discovery mechanism.
CoAP
Architecture
The
figure-1 depicts CoAP Architecture. As shown it
extends normal HTTP clients to clients having resource constraints. These
clients are known as CoAP clients. Proxy device bridges gap between constained
environment and typical internet environment based on HTTP protocols. Same
server takes care of both HTTP and CoAP protocol messages.
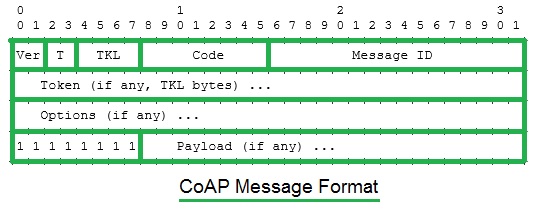
CoAP
Message Format | CoAP Header
The figure-2 depicts CoAP message format consists of 4 bytes header
followed by token value (from 0 to 8 bytes). The table below mentions header
which consists of 4 bytes i.e. 32 bits.
|
CoAP
message header |
Description |
|
Ver |
It is 2 bit unsigned integer.
It mentions CoAP version number. Set to one. |
|
T |
It is 2 bit unsigned integer.
Indicates message type viz. confirmable (0), non-confirmable (1), ACK (2) or
RESET(3). |
|
TKL |
It is 4 bit unsigned integer,
Indicates length of token (0 to 8 bytes). |
|
Code |
It is 8 bit unsigned integer,
It is split into two parts viz. 3 bit class (MSBs) and 5 bit detail (LSBs). |
|
Message ID |
16 bit unsigned integer. Used
for matching responses. Used to detect message duplication. |
CoAP
Protocol Message Exchanges
There are
two modes in which CoAP protocol messages get exchanged between CoAP client and
CoAP server viz. without separate response and with separate response.
With
separate response, server notifies client about receipt of the request message.
This will increase processing time but help in avoiding unnecessary
retransmissions.
CoAP IoT
is unreliable protocol due to use of UDP. Hence CoAP messages reach unordered
or will get lost when they arrive at destination.
To make
CoAP as reliable protocol, stop and wait with exponential backoff
retransmission feature is incorporated in it. Duplicate detection is also
introduced.
Difference between COAP and MQTT protocols
1. Constrained Application Protocol (COAP): The
constrained application protocol is a client server-based protocol. With this
protocol, the COAP packet can be shared between different client nodes which
are commanded by the COAP server. The server is responsible to share the
information depending on its logic but has not acknowledged it. This is used
with the applications which support the state transfer model.
2. Message Queuing Telemetry Transport
(MQTT): The message query telemetry transport protocol is a communication-based
protocol that is used for IoT devices. This protocol is based on the
publish-subscribe methodology in which clients receive the information through
a broker only to the subscribed topic. A broker is a mediator who categorizes
messages into labels before being delivered.
Difference between COAP and MQTT protocols:
|
Basis of |
COAP |
MQTT |
|
Abbreviation |
Constrained Application Protocol |
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport |
|
Communication Type |
It uses Request-Response model. |
It uses Publish-Subscribe model |
|
Messaging Mode |
This uses both Asynchronous and Synchronous. |
This uses only Asynchronous |
|
Transport layer protocol |
This mainly uses User Datagram protocol(UDP) |
This mainly uses Transmission Control protocol(TCP) |
|
Header size |
It has 4 bytes sized header |
It has 2 bytes sized header |
|
RESTful based |
Yes it uses REST principles |
No it does not uses REST principles |
|
Persistence support |
It does not has such support |
It supports and best used for live data
communication |
|
Message Labelling |
It provides by adding labels to the
messages. |
It has no such feature. |
|
Usability/Security |
It is used in Utility area networks and has
secured mechanism. |
It is used in IoT applications and is secure |
|
Effectiveness |
Effectiveness in LNN is excellent. |
Effectiveness in LNN is low. |
|
Communication Model |
Communication model is one-one. |
Communication model is many-many. |



Comments
Post a Comment